CelCradle系列生物反應器—高密度細胞培養的搖籃
一、什么是CelCradle生物反應器

CelCradle生物反應器根據潮汐漲落原理設計而成,其中波紋管的壓縮和解壓可使細胞不斷接觸培養基的營養與空氣,提供了一個低細胞撕裂、無泡沫、高氧氣飽和度以及高營養濃度的細胞培養環境。
CelCradle是用于高密度細胞培養的一款易于使用的經濟型臺式生物反應器,既可以高密度培養細胞,也可以收集細胞分泌產物。
二、CelCradle潮汐式工作原理
通過CelCradle細胞培養瓶底部的波紋管壓縮和解壓,細胞間歇的暴露在空氣和培養基中,使細胞充分與培養基和氧氣接觸,和滾瓶的原理類似。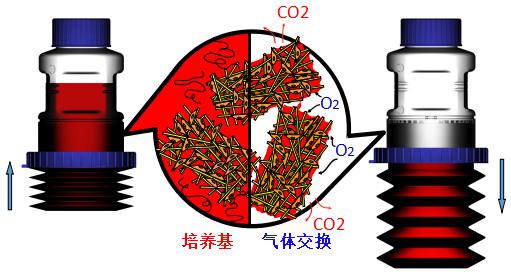
三、CelCradle生物反應器產品特點
•大面積高密度貼壁細胞培養空間
•預先滅菌、隨時可用
•一次性使用CelCradle培養瓶,操作簡單
•低剪切力、低細胞撕裂、無泡沫以及無氧氣限制高營養的細胞培養環境
•兼容大多數無血清培養基
•全細胞、細胞組分或細胞產物的培養和采集功能
四、為什么選擇CelCradle生物反應器
1. 簡便易用的設計,一次性使用可以節約空間和人力資源
CelCradle生物反應器是一款隨時可用的一次性生物反應系統,無需啟動時間及復雜的學習過程.
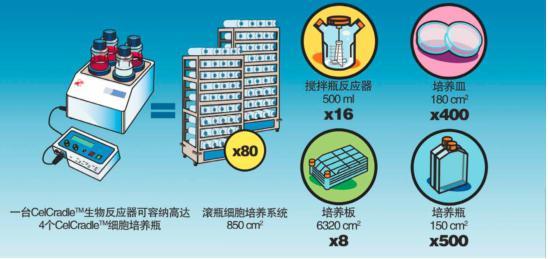
CelCradle生物反應器可放置在6立方英尺CO2培養箱內,并且可同時運行4個細胞培養瓶。 一個標準CelCradle細胞培養瓶帶有5.5g BioNoc II載體,可提供15000平方厘米的細胞培養總面積,培養細胞數可達到4~5 x 109/瓶,相當于18至20個滾動式細胞培養瓶的培養量。
可以通過增加CelCradle培養瓶數或者使用同為潮汐原理的TideCell生物反應器實現細胞規模的擴大化生產,從而簡化了培養系統規模擴大的過程以及節省了開發過程中所需的支出。
2. 高細胞產量,特殊的B_H功能促進蛋白表達
一臺CelCradle生物反應器可取代數百個培養皿、傳統細胞培養瓶以及多組細胞培養滾瓶等等,從而大大縮減生產成本。
該系統不僅可實現較高的細胞產量,且這種特殊的B_H功能(增加底部保持時間)不僅限制了細胞的過度生長而且增加了超過3倍的蛋白表達,同時還可實現更高的蛋白濃度并在培養過程中節省培養基。
五、應用領域
•哺乳動物和昆蟲細胞培養
•蛋白質和病毒生產
•單克隆抗體生產
•蛋白質組研究
•藥物研發
•藥物代謝動力學研究
•基因和細胞治療研究
專業論文支持
以下是一些現有支持CelCradle細胞培養系統的科學研究應用的學術論文
[1]Akiyama, M., Nakayama, D., Takeda, S., Kokame, K., Takagi, J., & Miyata, T. (n.d.). Crystal structure and enzymatic activity of an ADAMTS-13 mutant with the East Asian-specific P475S polymorphism. J Thromb Haemost Journal of Thrombosis and Haemostasis, 1399-1406.
[2]Asaoka, Y., Tanaka, T., Tsumoto, K., Tomita, M., & Ide, T. (n.d.). Efficient expression of recombinant soluble human FcγRI in mammalian cells and its characterization. Protein Expression and Purification, 155-161.
[3]Brown, A., Mcsharry, J., Adams, J., Kulawy, R., Barnard, R., Newhard, W., . . . Drusano, G. (2011). Pharmacodynamic Analysis of a Serine Protease Inhibitor, MK-4519, against Hepatitis C Virus Using a Novel In Vitro Pharmacodynamic System. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 1170-1181.
[4]Chen, Y., Wu, J., Wang, K., Chiang, Y., Lai, C., Chung, Y., & Hu, Y. (n.d.). Baculovirus-mediated production of HDV-like particles in BHK cells using a novel oscillating bioreactor. Journal of Biotechnology, 135-147.
[5]Drugmand, J., J.-F., J., Agathos, S., & Schneider, Y. (n.d.). Growth of Mammalian and Lepidopteran Cells on BioNOC II Disks, a Novel Macroporous Microcarrier. Cell Technology for Cell Products, 781-784.
[6]Hammonds, J., Chen, X., Zhang, X., Lee, F., & Spearman, P. (n.d.). Advances in methods for the production, purification, and characterization of HIV-1 Gag–Env pseudovirion vaccines. Vaccine, 8036-8048.
[7]Haredy, A., Takenaka, N., Yamada, H., Sakoda, Y., Okamatsu, M., Yamamoto, N., . . . Okamoto, S. (2013). An MDCK Cell Culture-Derived Formalin-Inactivated Influenza Virus Whole-Virion Vaccine from an Influenza Virus Library Confers Cross-Protective Immunity by Intranasal Administration in Mice. Clinical and Vaccine Immunology, 998-1007.
[8]Haredy, A., Yamada, H., Sakoda, Y., Okamatsu, M., Yamamoto, N., Omasa, T., . . . Yamanishi, K. (2014). Neuraminidase gene homology contributes to the protective activity of influenza vaccines prepared from the influenza virus library. Journal of General Virology, 2365-2371.
[9]Ho, L., Greene, C., Schmidt, A., & Huang, L. (n.d.). Cultivation of HEK 293 cell line and production of a member of the superfamily of G-protein coupled receptors for drug discovery applications using a highly efficient novel bioreactor. Cytotechnology, 117-123.
[10]Hu, Y., Lu, J., & Chung, Y. (n.d.). High-density cultivation of insect cells and production of recombinant baculovirus using a novel oscillating bioreactor. Cytotechnology, 145-153.
有興趣進一步了解我們CelCradle系列生物反應器的顧客可以通過以下聯系方式咨詢我們:
Mobile:010-5823 6368/5823 6468
Email:mail@escolifesciences.cn
Website: www.escolifesciences.cn