
單分子及熒光技術在生物學與醫學中的應用學術研討會
暨全國第七屆醫學生物物理學術會議
會議名稱:單分子及熒光技術在生物學與醫學中的應用學術研討會
會議主席:鐘桂生教授(上海科技大學生命學院、iHuman研究所)
時間:2016年4月7~8日
地點:上海市浦東新區張江高科技園區,海科路100號,上海科技大學、iHuman研究所內
主辦:上海市科學技術協會、上海市生物物理學會
承辦:上海科技大學生命學院、iHuman研究所
會議秘書長兼聯絡:上海市生物物理學會辦公室主任施永德教授(info@ssbiophysics.com.cn)
單分子和熒光技術是一門前沿科學,是揭示生命本質的重要手段;同時是一門復雜的技術,涉及熒光基團的設計與標記、儀器硬件與軟件的原理與應用。單分子與熒光技術還是一門藝術,通過高分辨率圖片與影像的拍攝,捕捉單分子的形態和動態變化,以精彩的圖像向人們展示生命活動的本質。
此次會議圍繞單分子與熒光技術,力求將科技與藝術有機結合,讓有志于本領域或對本領域有興趣的同仁一起交流最新的技術、試劑、儀器設備、展示獲得的科學研究成果和精彩的生物大分子圖片與動態的分子影像。同時讓從事相關試劑、儀器、設備研發的公司廠商展示其開發的最新產品,打造分子熒光領域專業的產學研平臺。歡迎各位同仁踴躍投稿,并展示拍攝的圖片和影像,也歡迎有關公司廠商展示新技術、新產品、新試劑。
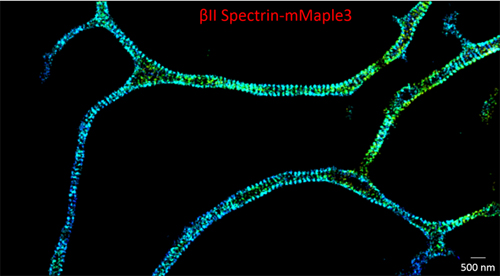
圖為本次會議主席鐘桂生教授用STORM拍攝的活神經元中的細胞骨架周期性結構圖片
會議內容包括:
1、邀請著名科學家,做單分子和熒光技術在生物科學和醫學領域相關研究進展的綜述報告,尤其是該技術在揭示細胞、亞細胞及分子水平的結構與功能的應用;
2、征集并展示相關領域科技工作者的論文摘要、圖片和影像;
3、組織專家委員會對科學墻報進行評獎,授予獲獎證書和獎金;
4、邀請分子熒光技術制造商,介紹最新的試劑、硬件、軟件以及使用方法;
5、成立單分子和熒光技術專業委員會,制定今后學術活動計劃;
大會初步特邀報告人及其論題:
·鐘桂生教授(上海科技大學、iHuman研究所):單分子熒光技術及其在醫學生物學中應用
·張東才教授(香港中文大學):Using fluorescent protein as a molecular maker of bio-sensor to study apoptotic signaling mechanism in a living cell (應用熒光標記蛋白作為生物敏感器的分子標記物研究活細胞凋亡過程中的信號發放機制)
·李明教授(中科院生物物理研究所):High precision single-molecule studies of molecular motor and bio-member (分子馬達和生物膜高精度單分子研究)
·畢國強教授(中國科技大學):Optical imaging of neuronal structure and dynamics(用光學成像的方法研究神經元結構與動態變化)
·鐘超教授(上海科技大學):Molecular imaging and nanomechanical characterization of self-assembling and multi-compositional amyloid nanofibers (淀粉樣蛋白纖維的自組裝與多組分結構的分子成像與納米機械力學特性的鑒定)
·劉建偉教授(復旦大學):題目待定
·孫博教授(上海科技大學):Single-molecular studies of bacteriophage T7 replisome(噬菌體T7的復制小體的單分子研究)
·王宏達教授(中科院長春應用化學研究所):單分子技術研究細胞膜結構與動態功能
·趙永芳教授(中科院生物物理研究所):利用單分子FRET研究跨膜轉運蛋白的結構與功能
·孫育杰教授(北京大學):Single Molecule Study of Chromatin DNA(染色質DNA單分子研究)
·高影教授(國家蛋白質科學中心•上海):Dissect Single Protein Folding by Using High-Resolution Optical Tweezers(用高分辨率光鑷解讀蛋白質折疊)
本次會議征集論文摘要、科學墻報、圖片、影像分類提綱
1、單分子和熒光技術進展及其在醫學生物學中的應用
2、熒光技術在細胞生物學與神經生物學中的應用(如神經元的突觸結構和動態變化、細胞凋亡、細胞分裂等)
3、熒光化學基礎研究及其在醫學生物學中應用進展
4、熒光技術在生物化學與分子生物學中的應用(如DNA的HRM高分辨率“熔解”曲線、熒光光譜、熒光偏振等)
5、熒光技術在基礎醫學、診斷醫學、臨床醫學中的應用
6、單分子與熒光成像的結合在醫學生物學中的應用
7、單分子和熒光成像設施物理硬件與軟件及其在醫學生物學中應用進展研究
8、熒光技術在微生物與環境科學中的應用(如水源微生物檢測)
9、其他熒光醫學生物學問題
(作者投稿自選以上分類提綱)
投稿文字:中文或英文
投稿截止日期:2016年3月15日下午5:00
投稿方式:摘要電子版投稿方法(用WORD格式書寫,列行與分段如下):
題目
作者及其次序,用*標明通訊作者,用下劃線標明報告作者
作者單位與郵政編碼
提供本文聯絡電子郵件地址
摘要:(1)目的;(2)方法;(3)結果;(4)結論。綜述性摘要格式可以自定。
摘要總長不超過A4半頁
投:info@ssbiophysics.com.cn
說明:除上述特邀報告以外,因會議時間與會場關系,其他的所有論文摘要內容一律用科學墻報展出,希望科學墻報設計中充分展示熒光圖片,本會對每一個科學墻報的論題支持稿費200元人民幣,還對其中優秀的進行評獎,對獲獎者頒發獎證和獎金。
摘要書寫樣板如下
Using fluorescent protein as a molecular marker/bio-sensor to study apoptotic signaling mechanism in a living cell
Donald C. Chang 張東才
Division of Life Science, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology
ClearWaterBay, Hong Kong, China
Email: bochang@ust.hk
To illustrate the power of using fluorescent proteins in solving important problems in life science, I present here several of our research projects as examples. We have developed special biophotonic techniques to study the dynamic properties of signaling proteins in a single living cell. Such a study allowed us to gain new insight into the signaling mechanism that regulates programmed cell death.Apoptosis (programmed cell death) is a very important cellular process that plays an important role in many diseases, including cancer, Alzheimer’s disease and auto-immune diseases.Improved understanding of the molecular signaling mechanisms of apoptosis will provide new drug targets for treating cancer or neurodegenerative diseases. In this talk, I will summarize our research in three related areas: (1) Using biophotonic techniques to monitor the dynamic movement and interaction of signaling proteins within an intact living cell. A key process in apoptosis is the permeabilization of mitochondrial outer membrane. This process is controlled by the remodeling of two proapoptotic Bcl-2 family proteins, Bax and Bak. At present, the molecular mechanism of this process is not clear. In this study, we used gene fusion to label Bax and Bak with CFP and YFP, respectively. Then, using a confocal microscope, we monitored the dynamic changes of protein distribution and protein-protein interaction of Bax and Bak during UV-induced apoptosis. Such study allows us to gain an insight on the molecular mechanism of triggering mitochondrial dysfunction during apoptosis. (2) Based on the fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) method, we have developed novel molecular bio-sensors for detecting caspase-3 (and caspase-8) activation within a single living cell. These sensors provide a powerful tool for rapid screening of new drugs. (3) Using this innovative technique, we have identified a number of anti-cancer compounds in TCM (traditional Chinese medicine), some of which can induce apoptosis in cancer cells by first arresting them in mitosis. These compounds (and their derivatives) have a strong potential to be developed into novel anti-cancer drugs. Using our biosensors, we can also screen for compounds isolated from TCM that prevent neuronal cell death. These compounds are candidates for new neuroprotective drugs.
科學墻報制作與展出
展板:寬度60厘米,高度120厘米。科學墻報的文字、格式、圖表均由作者自行設計。每一論題的科學墻報發稿費200元,在展出時發給作者簽收(如缺席,則示放棄)。本會將組織專家組對優秀科學墻報進行評獎,對獲獎者另行頒發獎證和獎金。
外地參會者建議住宿賓館:
(1)上海市徐匯區肇嘉浜路500號好望角大酒店(4星級,即中科院上海學術活動中心,靠近中科院生命科學研究院生化細胞所、神經所、營養所、健康所、巴士德所),單人間每夜380元(含早)、雙人標準間每夜460元(含早)。賓館電話021-64716060,自己乘公交車或地鐵赴會場。
(2)上海浦東新區科苑路1500號國際人才城酒店(4星級。靠近上海科技大學、國家蛋白質科學中心、應用物理研究所同步輻射光源、曙光醫院),雙床或大單床標準間,每夜468元(含早),電話:021-61651111,離開會場很近,只需步行。
初步議程:
4月7日:外地代表住進如上賓館
4月8日上午:8:00~9:00報到注冊,公司布展,代表貼科學墻報(上海市浦東新區張江高科技園區,海科路100號,上海科技大學大報告廳的入口處)
上午9:00~12:00特邀報告(中間有拍集體照與茶歇)
下午12:00~13:30午餐,觀看科學墻報(會議對墻報作者發出稿費)、展覽會、專家組評出優秀科學墻報
下午13:30~17:30特邀報告,專家組宣布科學墻報授獎者名單,頒發獎證與獎金(中間有茶歇)
下午17:30~ 晚餐
專家組會議并集體用餐17:30~
點擊下載: 參會回執_第七屆醫學生物物理學術會議.doc 參會回執_第七屆醫學生物物理學術會議.doc | 








